3D printing is a process of
manufacturing a three-dimensional solid object or assembly part from a digital
3D CAD model. It is an additive manufacturing process where an object is
created by depositing, laying down, or solidifying successive layers of material
to transform a digital file into a 3D object under a computer-controlled
process. Different technologies and methods such as material extrusion, vat
polymerization, bed fusion, and Stereolithography are used for 3D
Printing.
Stereolithography or SLA
3D printing is one of the most advanced and accurate printing processes to create
three-dimensional objects using digital CAD files. It is an additive
manufacturing technique that uses a high-powered laser to harden liquid
photopolymer resin to form a desired solid shape. As a widely recognized
industrial 3D printing process, SLA 3D printing is used to manufacture complex
models, assembly parts, and prototypes with high accuracy and excellent surface
finish.
How
does it work?
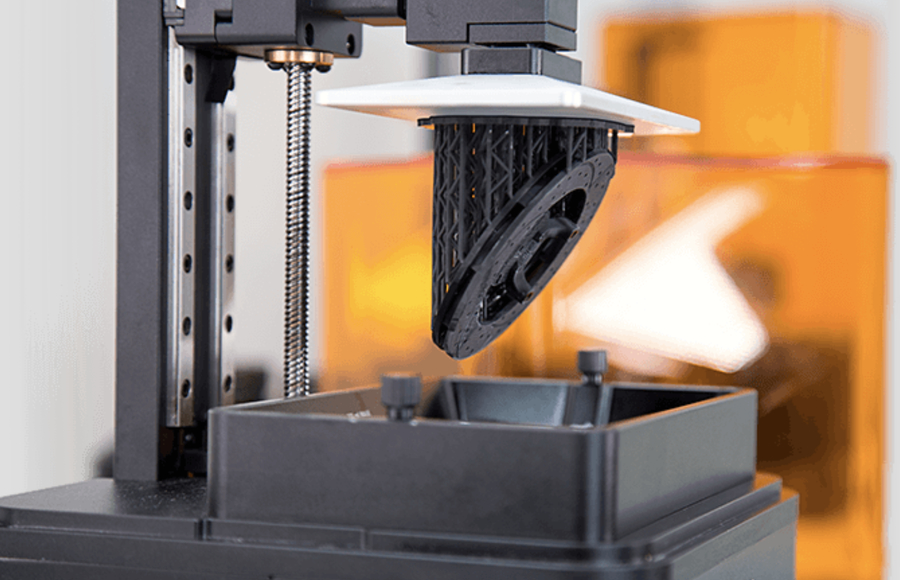
The basic components of an
SLA 3D printer include a tank filled with the photopolymer resin, a perforated
platform, an ultraviolet laser, and a computer interface to complete the whole
process. The SLA 3D printing workflow combines the three basic processes –
design, printing, and post-process to create a physical object.
Design:
In any additive
manufacturing process, 3D designing is the first step using CAD software. A CAD
engineer or 3D designer incorporates every detail, measurement, and
specification as per the requirements to design a 3D model in the digital
format. After designing the concept using CAD software, the CAD files are
exported in a 3D printable digital file (STL or OBJ file).
STL (standard tessellation/triangle language) files are the most preferred digital file formats for 3D object printing. STL digital files every detail of the object such as the geometry of the 3D object and other required attributes.
SLA
3D Printing:
A standard SLA printer
includes a3D slider software to configure the pre-printing settings to feed an
STL file for generating G-code language for 3D printers. It is an important
step to slice the digital model into layers for additive printing. Once the
initial settings and setups are completed, the printing software sends the
instruction to the SLA printer to begin the layered printing process.
The high-powered lasers in
the 3D printer solidify each layer of the digital model using the photopolymer
resin until the whole object is created. The laser solidifies the liquid resin
where it hits as per the uploaded design into the software. A computer
interface controls and manages the laser to design the appropriate coordinates
as per the digital feed.
Post-processing:
Once the 3D printing
process is completed, any uncured or excess resin is removed from the object
surface using isopropyl alcohol. Post-curing is the next step that enables the
object to achieve the highest possible accuracy, strength, and stability.
Post-processing also involves some additional steps depending on the material
type and part to get a high surface finish as per the industrial requirements.
So, this is how the SLA 3D
printing process is done that requires a high level of skill, knowledge, and
expertise at all levels to create a highly accurate and high finish object. If
you are looking for Industrial additive manufacturing, you should look for a
reputed and experienced company that has expertise in SLA
3D printing in China for your applications.
A professional and
qualified team can help you out with your 3D designs and feeds to get the right
settings for 3D printing your industrial applications. They ensure to meet your
expectations with every little detail right from designing to post-processing
to achieve the best results.
















